6.4 KiB
Contribute to Terraform AzureRM provider
This document describe how you can get ready to contribute to the AzureRM Terraform provider.
Setup your system
Terraform
You need to install Terraform on your dev environment. You can downlaod it from this page.
Go tools
Terraform is developed using Go. You need to install Go 1.11.x to be able to build and debug the provider locally. You can download it from this page and find the installation instructions for your system here
Then you can test your environment following the instructions on this page.
Check you GOPATH
As of many Go project, AzureRM Terraform provider rely on your GOPATH environment variable. You may want to make sure it is well configured for your system, reading this page.
Visual Studio Code
You can use the IDE you love, but in this documentation we will describe how to contribute to the Terraform AzureRM provider using Visual Studio Code. You can download it for your system from this page.
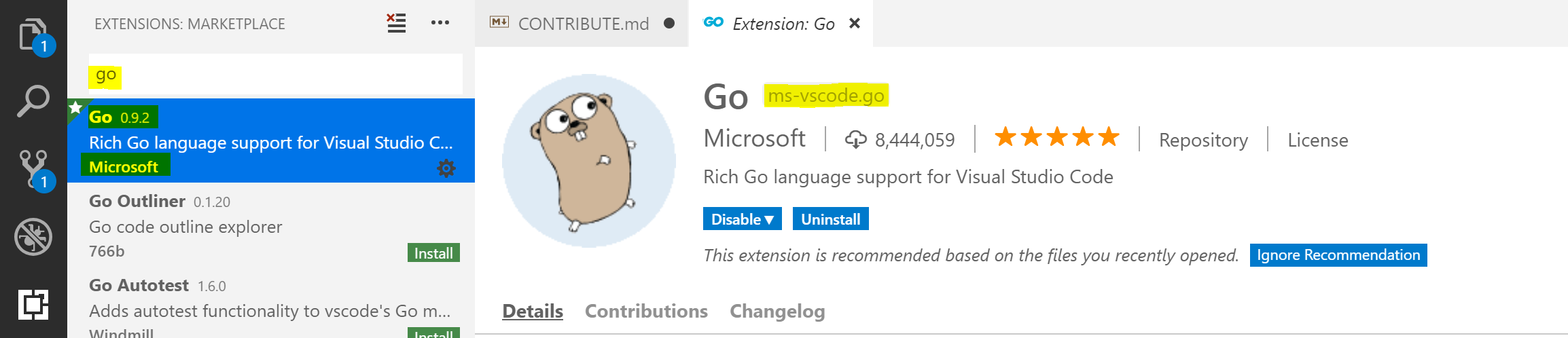
Once installed, download the Go extension for VS Code:
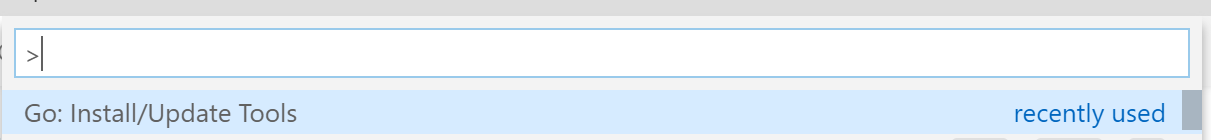
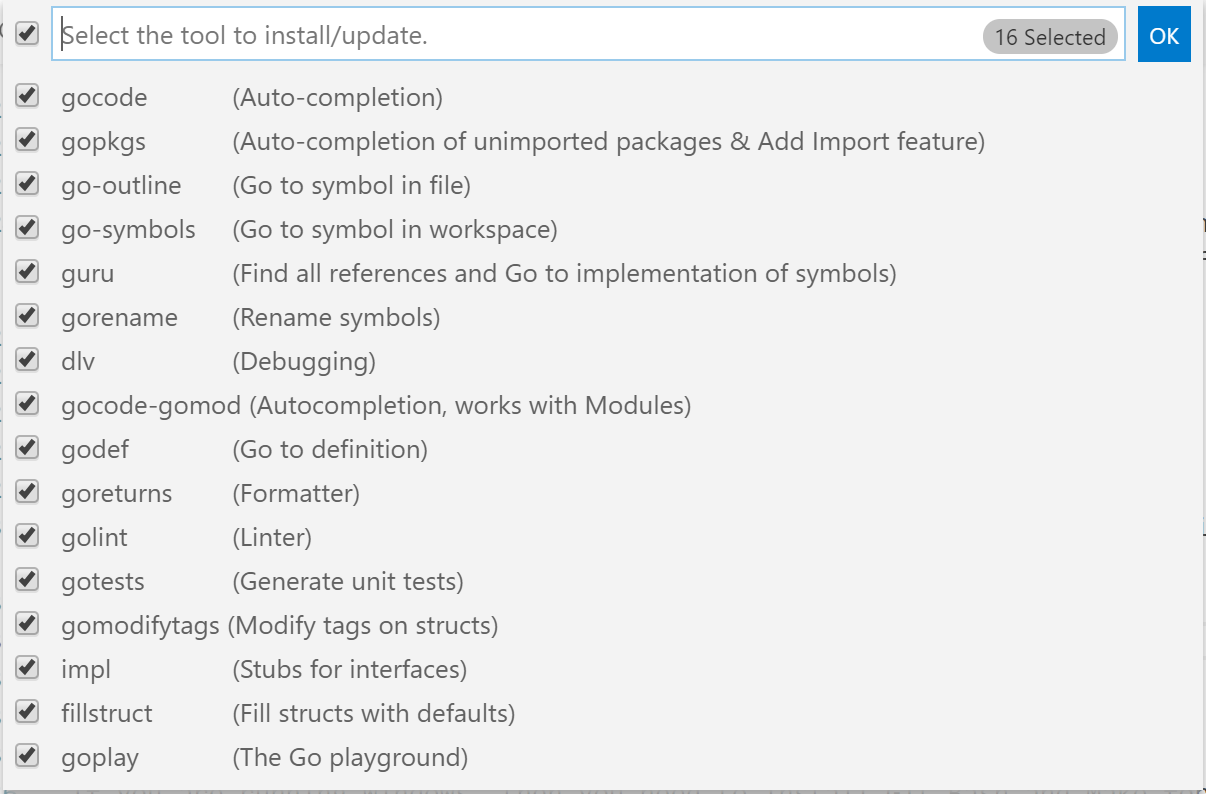
Once installed, open VS Code and look for the Go: Install/Update Tools in the command palette, a select all the tools:
Specific requirements for Windows users
If you are running Windows, then you need to install Git Bash and Make for Windows. Check the dedicated section on Terraform on Azure repository here.
Get the sources
First, go to the AzureRM Terraform provider project page and fork the repository into your GitHub account.
Once done, you need to clone your fork into the $GOPATH/src/github.com/terraform-providers/terraform-provider-azurerm folder.
Build the sources
You can check that everything is OK by building the AzureRM provider:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/terraform-providers/terraform-provider-azurerm
make build
Once completed, the binary of the AzureRM provider should be available in the $GOPATH/bin directory.
Note: on Windows, you need to use Git Bash
More information here.
Work with your local build
Once you have built a new version of the AzureRM Terraform provider, you can use it locally.
To use your local version, the first thing to do is a terraform init, as usual, to inialize your terraform working directory.
The init operation will download the AzureRM Provider for you. You can just remove it, and replace it with your local copy.
Do a terraform init again and you're done ! :-)
Debug the AzureRM provider using Visual Studio Code and Delve
It is possible to use Visual Studio Code and Delve (the Golang debugger) to debug the AzureRM provider. The easiest way to debug Terraform AzureRM Provider is to execute the acceptances unit test with the Delve debugger attached. Acceptance tests are tests that are written for every resources and data sources and that will really execute the code to an Azure subscription, to validate everything is working well.
First, to be able to connect to Azure, you need to create a service principal using the following command:
az ad sp create-for-rbac --role=Contributor --scope=/subscriptions/<YOUR_SUBSCRIPTION_ID>
Then, you need to create a .launch.json file inside the .vscode folder at the root of the Terraform AzureRM provider directory (create the .vscode folder if it does not exist).
Copy the following content into the file:
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Launch test function",
"type": "go",
"request": "launch",
"mode": "test",
"program": "${workspaceRoot}/azurerm/resource_arm_container_registry_test.go",
"args": [
"-test.v",
"-test.run",
"TestAccAzureRMContainerRegistry_geoReplication"
],
"envFile": "${workspaceRoot}/.vscode/private.env",
"showLog": true
},
]
}
The configuration above allows to start debugging a Terraform resource, by launching one or more acceptance test:
- The
programproperty indicates the file you want to debug - The last entry of the
argsproperty, hereTestAccAzureRMContainerRegistry_geoReplicationrepresents th test to launch. You can use regex to run multiple tests (ex:TestAccAzureRMContainerRegistry_*) - The
envFileproperty defines the path to get the environment variables file (mainly Azure credentials) that needs to be used to run the acceptance test.
Create the private.env file into the .vscode folder and fill it with the following environment variables:
ARM_CLIENT_ID=<YOUR_SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_CLIENT_ID>
ARM_CLIENT_SECRET=<YOUR_SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_CLIENT_SECRET>
ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID=<YOUR_AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID>
ARM_TENANT_ID=<YOUR_AZURE_TENANT_ID>
ARM_TEST_LOCATION=<AZURE_LOCATION_1>
ARM_TEST_LOCATION_ALT=<AZURE_LOCATION_2>
TF_ACC=1
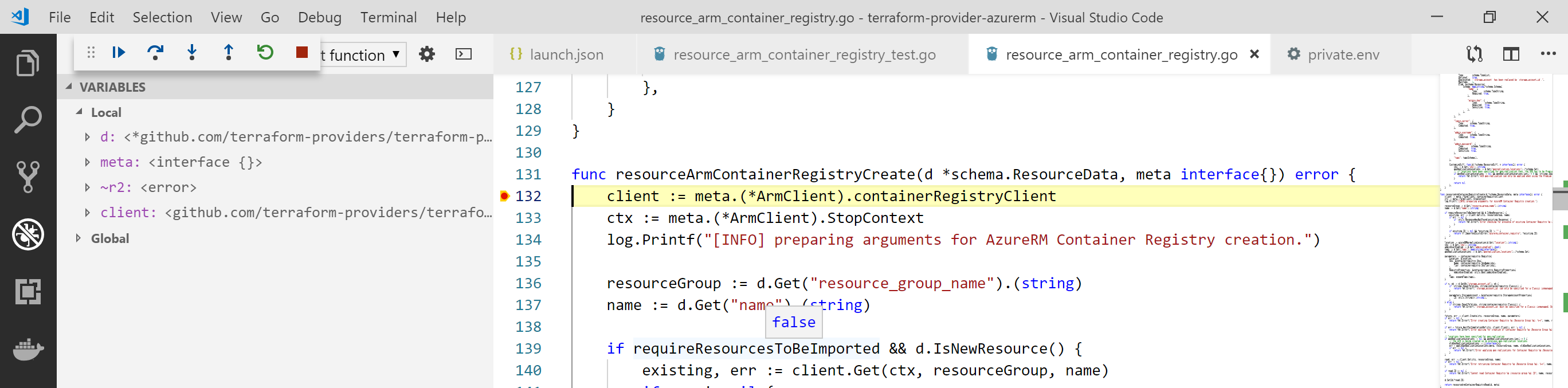
Once done, you can just press F5 and the debug will start! You can place breakpoints in your code to do step by step debugging:
Note: the first time your start the debug, it can take a while, you need to be patient :-)
Other
Slack
You can request an invite to access the Terraform on Azure Slack here.